
by codm | May 26, 2023 | Newsletter
After four years of follow-up, LENVIMA plus KEYTRUDA reduced the risk of death by 21% versus sunitinib in the pivotal Phase 3 CLEAR (Study 307)/KEYNOTE-581 trial
Final results will be presented at ASCO 2023 in an oral abstract session
For Print (PDF)
TOKYO and RAHWAY, N.J., May.26, 2023 – Eisai (Headquarters: Tokyo, CEO: Haruo Naito) and Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA (known as MSD outside of the United States and Canada) today announced data from the final pre-specified overall survival (OS) analysis of the pivotal Phase 3 CLEAR (Study 307)/KEYNOTE-581 trial investigating LENVIMA, the orally available multiple receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor discovered by Eisai, plus KEYTRUDA, Merck’s anti-PD-1 therapy, for the first-line treatment of patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC). These data will be presented on Monday, June 5 at 11:54 a.m. Central Daylight Time during an oral abstract session at the 2023 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting (Abstract #4502).
After four years of follow-up, LENVIMA plus KEYTRUDA maintained a clinically meaningful OS benefit versus sunitinib, reducing the risk of death by 21% (HR=0.79 [95% CI, 0.63-0.99]). The 24- and 36-month estimated OS rates were 80.4% and 66.4% for LENVIMA plus KEYTRUDA versus 69.6% and 60.2% for sunitinib, respectively. Results from the final pre-specified OS analysis were consistent with the superior results versus sunitinib from the primary OS analysis of the CLEAR/KEYNOTE-581 trial.
Additionally, LENVIMA plus KEYTRUDA reduced the risk of disease progression or death by 53% (HR=0.47 [95% CI, 0.38-0.57]), with a median progression-free survival (PFS) of 23.9 months (95% CI, 20.8-27.7) for LENVIMA plus KEYTRUDA versus 9.2 months (95% CI, 6.0-11.0) for sunitinib; the objective response rate (ORR) was 71.3% (95% CI, 66.6-76.0) with a complete response (CR) rate of 18.3% for LENVIMA plus KEYTRUDA versus an ORR of 36.7% (95% CI, 31.7-41.7) with a CR rate of 4.8% for sunitinib.
There were no new safety signals and the safety profile at the final OS analysis was consistent with the primary analysis. Grade ≥3 treatment-related adverse events (TRAE) occurred in 74.1% of patients who received LENVIMA plus KEYTRUDA versus 60.3% of patients who received sunitinib. The six most common TRAEs of any grade of patients in the LENVIMA plus KEYTRUDA arm were diarrhea (56.0%), hypertension (54.3%), hypothyroidism (44.9%), decreased appetite (35.5%), fatigue (34.1%) and stomatitis (32.7%). In the sunitinib arm, the six most common TRAEs of any grade were diarrhea (45.3%), hypertension (40.3%), stomatitis (37.4%), palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia (36.2%), fatigue (32.9%) and nausea (28.2%).
“LENVIMA plus KEYTRUDA continues to demonstrate durable clinical benefit as a first-line treatment for patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma, as shown by the clinically meaningful improvement in overall survival sustained with four years of follow up,” said Dr. Thomas Hutson, DO, Pharm.D., FACP, Director of the Urologic Oncology Program and Co-chair of the Urologic Cancer Research and Treatment Center, Texas Oncology at Baylor Sammons Cancer Center. “Furthermore, these data also showed clinically meaningful improvements in median PFS and ORR compared to sunitinib. These findings reinforce the important role of LENVIMA plus KEYTRUDA as a first-line standard of care treatment option for patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma.”
“Long-term follow up data from the CLEAR/KEYNOTE-581 trial show the responses to first-line use of KEYTRUDA plus LENVIMA were durable for many of these patients,” said Dr. Gregory Lubiniecki, Vice President, Global Clinical Development, Merck Research Laboratories. “Through our joint clinical development program with Eisai, we’re continuing to advance our research evaluating KEYTRUDA plus LENVIMA for other challenging cancers as we strive to help even more patients.”
“At the final pre-specified analysis, LENVIMA plus KEYTRUDA continued to demonstrate clinically meaningful efficacy across PFS, ORR and OS, providing patients and their physicians with new information about treating people living with advanced renal cell carcinoma,” said Corina Dutcus, M.D., Senior Vice President, Clinical Development, Oncology at Eisai Inc. “These results are a testament to our steadfast commitment to people living with advanced cancers, and we are grateful for the support from the patients, families and healthcare provider community for their participation in this research.”
LENVIMA plus KEYTRUDA is approved in the U.S., the EU, Japan and other countries for the treatment of advanced RCC and certain types of advanced endometrial carcinoma. Lenvatinib is marketed as KISPLYX® for advanced RCC in the EU. Eisai and Merck are studying the LENVIMA plus KEYTRUDA combination through the LEAP (LEnvatinib And Pembrolizumab) clinical program in various tumor types, including but not limited to endometrial carcinoma, hepatocellular carcinoma, non-small cell lung cancer, RCC, head and neck cancer, gastric cancer and esophageal cancer across multiple clinical trials.
Investor Contacts:
| Eisai Co., Ltd. |
Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA |
|
Public Relations:
+81-(0)3-3817-5120
Investor Relations:
+81-(0) 3-3817-5122
|
Media Relations
Julie Cunningham: +1-(617) 519-6264
John Infanti: +1-(609) 500-4714
Investor Relations
Peter Dannenbaum: +1-(732) 594-1579
Damini Chokshi: +1-(732) 594-1577
|
Study design and additional data from CLEAR/KEYNOTE-581
The CLEAR/KEYNOTE-581 trial is a multicenter, randomized, open-label Phase 3 trial (ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT02811861) evaluating LENVIMA in combination with KEYTRUDA or in combination with everolimus versus sunitinib for the first-line treatment of patients with advanced RCC. The major efficacy outcome measures were PFS, as assessed by independent radiologic review (IRC) according to Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors version 1.1 (RECIST v1.1), and OS. Additional efficacy outcome measures included confirmed ORR as assessed by IRC, health-related quality of life (HRQoL) and safety.
The trial enrolled 1,069 patients who were randomized 1:1:1 to receive LENVIMA (20 mg orally once daily) plus KEYTRUDA (200 mg intravenously every three weeks for up to 24 months), or LENVIMA (18 mg orally once daily) plus everolimus (5 mg orally once daily), or sunitinib (50 mg orally once daily for four weeks on treatment, followed by two weeks off treatment). KEYTRUDA was administered for up to 35 cycles (approximately two years) or until protocol-specified discontinuation criteria were met. After completing two years of combination therapy, LENVIMA may have been administered as a single agent until protocol-specified discontinuation criteria were met.
This final pre-specified OS analysis was event driven and was triggered by approximately 304 OS target events in the two treatment arms (149 events out of 355 patients for KEYTRUDA plus LENVIMA versus 159 events out of 357 patients for sunitinib).
The median duration of response was 26.7 months (95% CI, 22.8-34.6) for LENVIMA plus KEYTRUDA versus 14.7 months (95% CI, 9.4-18.2) for sunitinib.
Efficacy results were consistent across the pre-specified Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSKCC) risk groups (favorable, intermediate and poor) and International Metastatic RCC Database Consortium (IMDC) risk groups. Across the pre-specified Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSKCC) risk groups (favorable, intermediate and poor), OS and PFS were improved with LENVIMA plus KEYTRUDA versus sunitinib. Interpretation OS in favorable risk patients is limited by low number of events.
Fewer patients who were treated with LENVIMA plus KEYTRUDA received subsequent anti-cancer therapies (181 out of 355 patients, 51.0%) versus those who were treated with sunitinib (246 out of 357 patients, 68.9%), with 56 patients (15.8%) and 195 patients (54.6%) who went on to receive PD-1/PD-L1 checkpoint inhibitors, respectively. In an exploratory analysis using a 2-stage model, LENVIMA plus KEYTRUDA reduced the risk of death by 45% versus sunitinib when adjusted for subsequent anticancer medications (HR=0.55 [95% CI, 0.44-0.69]).
About renal cell carcinoma (RCC)
Worldwide, it is estimated there were more than 431,000 new cases of kidney cancer diagnosed and more than 179,000 deaths from the disease in 2020. 1 Renal cell carcinoma is by far the most common type of kidney cancer; about nine out of 10 kidney cancer diagnoses are RCC. 2 Renal cell carcinoma is about twice as common in men as in women. 3 Most cases of RCC are discovered incidentally during imaging tests for other abdominal diseases.4 Approximately 30% of patients with RCC will have metastatic disease at diagnosis. 4 Survival is highly dependent on the stage at diagnosis, and the five-year survival rate is 15% for patients diagnosed with metastatic disease. 5
About LENVIMA® (lenvatinib) Capsules
LENVIMA, discovered and developed by Eisai, is an orally available multiple receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor that inhibits the kinase activities of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptors VEGFR1 (FLT1), VEGFR2 (KDR), and VEGFR3 (FLT4). LENVIMA inhibits other kinases that have been implicated in pathogenic angiogenesis, tumor growth, and cancer progression in addition to their normal cellular functions, including fibroblast growth factor (FGF) receptors FGFR1-4, the platelet derived growth factor receptor alpha (PDGFRα), KIT, and RET. In syngeneic mouse tumor models, LENVIMA decreased tumor-associated macrophages, increased activated cytotoxic T cells, and demonstrated greater antitumor activity in combination with an anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody compared to either treatment alone. LENVIMA has been approved for the indications below.
Thyroid cancer
・Indication as monotherapy
(Approved in over 80 countries including Japan, the United States, China, and countries in Europe and Asia)
Japan: Unresectable thyroid cancer
The United States: The treatment of patients with locally recurrent or metastatic, progressive, radioiodine-refractory differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC)
Europe: The treatment of adult patients with progressive, locally advanced or metastatic, differentiated (papillary/follicular/Hürthle cell) thyroid carcinoma (DTC), refractory to radioactive iodine (RAI)
Hepatocellular carcinoma
・Indication as monotherapy
(Approved in over 80 countries including Japan, the United States, China, and countries in Europe and Asia)
Japan: Unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma
The United States: The first-line treatment of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)
Europe: The treatment of adult patients with advanced or unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) who have received no prior systemic therapy
Thymic carcinoma
・Indication as monotherapy (Approved in Japan)
Japan: Unresectable thymic carcinoma
Renal cell carcinoma (In Europe, the agent was launched under the brand name Kisplyx®)
・Indication in combination with everolimus
(Approved in over 65 countries including the United States, and countries in Europe and Asia)
The United States: The treatment of adult patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC) following one prior anti-angiogenic therapy
Europe: The treatment of adult patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma following one prior vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) targeted therapy
・Indication in combination with KEYTRUDA
(Approved in over 45 countries including Japan, the United States, and countries in Europe and Asia)
Japan: Radically unresectable or metastatic renal cell carcinoma
The United States: The first-line treatment of adult patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma
Europe: The first-line treatment of adult patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma
Endometrial carcinoma
・Indication in combination with KEYTRUDA
(Approved [including conditional approval] in over 45 countries including Japan, the United States, and countries in Europe and Asia)
Japan: Unresectable, advanced or recurrent endometrial carcinoma that progressed after cancer chemotherapy
The United States: The treatment of patients with advanced endometrial carcinoma (EC) that is mismatch repair proficient (pMMR), as determined by an FDA-approved test, or not microsatellite instability-high (MSI-H), who have disease progression following prior systemic therapy in any setting and are not candidates for curative surgery or radiation.
Europe: The treatment of adult patients with advanced or recurrent endometrial carcinoma (EC) who have disease progression on or following prior treatment with a platinum-containing therapy in any setting and are not candidates for curative surgery
About KEYTRUDA® (pembrolizumab) Injection, 100mg
KEYTRUDA is an anti-programmed death receptor-1 (PD-1) therapy that works by increasing the ability of the body’s immune system to help detect and fight tumor cells. KEYTRUDA is a humanized monoclonal antibody that blocks the interaction between PD-1 and its ligands, PD-L1 and PD-L2, thereby activating T lymphocytes which may affect both tumor cells and healthy cells.
Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA has the industry’s largest immuno-oncology clinical research program. There are currently more than 1,600 trials studying KEYTRUDA across a wide variety of cancers and treatment settings. The KEYTRUDA clinical program seeks to understand the role of KEYTRUDA across cancers and the factors that may predict a patient’s likelihood of benefitting from treatment with KEYTRUDA, including exploring several different biomarkers.
About the Eisai and Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA Strategic Collaboration
In March 2018, Eisai and Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA, known as MSD outside the United States and Canada, through an affiliate, entered into a strategic collaboration for the worldwide co-development and co-commercialization of LENVIMA. Under the agreement, the companies will jointly develop, manufacture and commercialize LENVIMA, both as monotherapy and in combination with KEYTRUDA, the anti-PD-1 therapy from Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA.
In addition to ongoing clinical studies evaluating the LENVIMA plus KEYTRUDA combination across several different tumor types, the companies have jointly initiated clinical studies through the LEAP (LEnvatinib And Pembrolizumab) clinical program and are evaluating the combination in multiple tumor types across more than 10 clinical trials.
Eisai’s Focus on Cancer
Eisai acknowledges “Oncology” as one of its key strategic areas, and will continue to focus on the discovery and development of anti-cancer drugs within drug discovery domains including “microenvironment”, “proteostasis disruption”, “cell lineage and cell differentiation”, and “inflammation, hypoxia, oxidative stress and cell senescence” under the Deep Human Biology Learning (DHBL) drug discovery and development organization. Eisai aspires to discover innovative new drugs with new targets and mechanisms of action from these domains, with the aim of contributing to the cure of cancers.
About Eisai
Eisai’s Corporate Concept is “to give first thought to patients and people in the daily living domain, and to increase the benefits that health care provides.” Under this Concept [also known as our human health care (hhc) Concept], we aim to effectively achieve social good in the form of relieving anxiety over health and reducing health disparities. With a global network of R&D facilities, manufacturing sites and marketing subsidiaries, we strive to create and deliver innovative products to target diseases with high unmet medical needs, with a particular focus in our strategic areas of Neurology and Oncology.
In addition, our continued commitment to the elimination of neglected tropical diseases (NTDs), which is a target (3.3) of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), is demonstrated by our work on various activities together with global partners.
For more information about Eisai, please visit www.eisai.com (for global headquarters: Eisai. Co., Ltd.), us.eisai.com (for U.S. headquarters: Eisai, Inc.) or www.eisai.eu (for Europe, Middle East, Africa, Russia, Australia and New Zealand headquarters: Eisai Europe Ltd.), and connect with us on Twitter (U.. and global) and LinkedIn (for U.S. and EMEA).
Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA’s Focus on Cancer
Our goal is to translate breakthrough science into innovative oncology medicines to help people with cancer worldwide. At Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA, the potential to bring new hope to people with cancer drives our purpose and supporting accessibility to our cancer medicines is our commitment. As part of our focus on cancer, Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA is committed to exploring the potential of immuno-oncology with one of the largest development programs in the industry across more than 30 tumor types. We also continue to strengthen our portfolio through strategic acquisitions and are prioritizing the development of several promising oncology candidates with the potential to improve the treatment of advanced cancers. For more information about our oncology clinical trials, visit www.merck.com/clinicaltrials.
About Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, US
For over 130 years, Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA, known as MSD outside of the United States and Canada, has been inventing for life, bringing forward medicines and vaccines for many of the world’s most challenging diseases in pursuit of our mission to save and improve lives. We demonstrate our commitment to patients and population health by increasing access to health care through far-reaching policies, programs and partnerships. Today, Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA continues to be at the forefront of research to prevent and treat diseases that threaten people and animals – including cancer, infectious diseases such as HIV and Ebola, and emerging animal diseases – as we aspire to be the premier research-intensive biopharmaceutical company in the world. For more information, visit www.merck.com and connect with us on Twitter, Facebook, Instagram, YouTube and LinkedIn.
Forward-Looking Statement of Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA
This news release of Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA (the “company”) includes “forward-looking statements” within the meaning of the safe harbor provisions of the U.S. Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. These statements are based upon the current beliefs and expectations of the company’s management and are subject to significant risks and uncertainties. There can be no guarantees with respect to pipeline candidates that the candidates will receive the necessary regulatory approvals or that they will prove to be commercially successful. If underlying assumptions prove inaccurate or risks or uncertainties materialize, actual results may differ materially from those set forth in the forward-looking statements.
Risks and uncertainties include but are not limited to, general industry conditions and competition; general economic factors, including interest rate and currency exchange rate fluctuations; the impact of the global outbreak of novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19); the impact of pharmaceutical industry regulation and health care legislation in the United States and internationally; global trends toward health care cost containment; technological advances, new products and patents attained by competitors; challenges inherent in new product development, including obtaining regulatory approval; the company’s ability to accurately predict future market conditions; manufacturing difficulties or delays; financial instability of international economies and sovereign risk; dependence on the effectiveness of the company’s patents and other protections for innovative products; and the exposure to litigation, including patent litigation, and/or regulatory actions.
The company undertakes no obligation to publicly update any forward-looking statement, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise. Additional factors that could cause results to differ materially from those described in the forward-looking statements can be found in the company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2022 and the company’s other filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) available at the SEC’s Internet site (www.sec.gov).
1 International Agency for Research on Cancer, World Health Organization. “Kidney Fact Sheet.” Cancer Today, 2020. https://gco.iarc.fr/today/data/factsheets/cancers/29-Kidney-fact-sheet.pdf .
2 American Cancer Society. “What Is Kidney Cancer?” About Kidney Cancer.
https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/kidney-cancer/about/what-is-kidney-cancer.html .
3 American Cancer Society. “Key Statistics About Kidney Cancer” About Kidney Cancer. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/kidney-cancer/about/key-statistics.html .
4 American Family Physician. Renal Cell Carcinoma: Diagnosis and Management.
https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2019/0201/p179.html .
5 American Cancer Society. “Survival Rates for Kidney Cancer” Early detection, Diagnosis, and Staging.
https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/kidney-cancer/detection-diagnosis-staging/survival-rates.html

by codm | May 25, 2023 | Newsletter
For Print (PDF)
Eisai Co., Ltd. (Headquarters: Tokyo, CEO: Haruo Naito, “Eisai”) has announced that it will grant a total of 625 million yen to the Global Health Innovative Technology Fund (“GHIT Fund”) to fund the third phase of its activities, which will take place in the five-year period from FY2023 to FY2027. The GHIT Fund is a public-private partnership, co-established in April 2013 by partners such as Japanese pharmaceutical companies (including Eisai), the Japanese government, and the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, for the purpose of accelerating development of new medicines to cure infectious diseases in developing and emerging countries by facilitating collaboration between research organizations in Japan and overseas. Eisai has provided a total of 1 billion yen to the first phase (FY2013 – FY2017) and the second phase (FY2018 – FY2022) of the GHIT Fund.
In order to develop treatments for the numerous people suffering from infectious diseases such as neglected tropical diseases (NTDs) and malaria in developing and emerging countries, there are disease-specific development and marketability issues to overcome. It is also necessary to establish local supply systems and help patients secure access to diagnosis and treatments. The key to overcoming these challenges are industry-government-academia partnerships which transcend the usual sector boundaries.
Eisai considers making efforts to resolve the global issue of access to medicines to be its duty. Under a public-private partnership including governments, international organizations, and private non-profit organizations, Eisai has participated in 23 joint research projects to develop new medicines and vaccines for mycetoma, malaria and filariasis, with the support of the GHIT Fund.
Eisai has conducted a Phase II clinical trial of its in-house developed agent E1224 (generic name: fosravuconazole) in Sudan for the treatment of mycetoma in partnership with the non-profit organization Drugs for Neglected Diseases initiative (DNDi). Eisai is also conducting a Phase II clinical trial of antimalarial agent SJ733 in collaboration with the University of Kentucky.
Eisai considers efforts for improving access to medicines, such as the elimination of NTDs and malaria, as activities aimed at creating long-term corporate value and social impact based on its corporate concept of human health care (hhc). We will continue to strengthen cooperation with our global partners and contribute to “relieving anxiety over health” and “reducing health disparities” for people at risk of infection with NTDs and those suffering from theses diseases.
Media Inquiries:
Public Relations Department,
Eisai Co., Ltd.
+81-(0)3-3817-5120
[Notes to editors]
1. About the Global Health Innovative Technology Fund (GHIT Fund)
The GHIT Fund is a Japan-based international public-private partnership fund (PPP) that was formed between the Government of Japan, multiple pharmaceutical companies, the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, Wellcome, and the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP). The GHIT Fund invests in and manages an R&D portfolio of development partnerships aimed at addressing neglected diseases, such as malaria, tuberculosis, and neglected tropical diseases, which afflict the world’s vulnerable and underserved populations. In collaboration with global partners, the GHIT Fund mobilizes Japanese industry, academia, and research institutes to create new drugs, vaccines, and diagnostics for malaria, tuberculosis, and neglected tropical diseases.
https://www.ghitfund.org/en
2. About Neglected Tropical Diseases (NTDs)
Neglected Tropic Diseases (NTDs) include 20 diseases that the World Health Organization (WHO) identifies as tropical diseases which human race must overcome. More than 1.7 billion people living in the poorest and most marginalized communities worldwide are exposed to the risk of NTD infection. The spread of NTDs is mainly caused by poor hygienic conditions associated with poverty. Infections from these diseases may result in serious physical impairment and this often results in normal economic and social activities becoming highly challenging to the individual. In the worst cases, NTDs may also result in death. The prevalence of NTDs is a stumbling block to economic growth for developing and emerging countries.
The following 20 NTDs have been designated by the WHO for control or elimination: dengue fever and chikungunya, rabies, trachoma, buruli ulcer, endemic treponematoses (yaws), leprosy (Hansen’s disease), Chagas disease, African sleeping sickness (Human African trypanosomiasis), leishmaniasis, taeniasis/cysticercosis, dracunculiasis (guinea worm disease], echinococcosis, food-borne trematode infections, lymphatic filariasis, onchocerciasis, schistosomiasis, soil-transmitted helminthiasis, mycetoma, scabies and snakebite envenoming.
3. About Mycetoma
Mycetoma was officially recognized as the 18th NTD by the WHO in 2016. It is considered to be one of the most neglected tropical diseases since there is a lack of basic information including its transmission pathway and incidence. Mycetoma is a progressive, chronic subcutaneous infectious disease. While most commonly seen in the feet, it can also occur in other parts of the body. It is caused by bacteria or fungus entering the body through a cut or wound and infecting the tissue beneath the skin.1
Mycetoma is divided into two subtypes: Actinomycetoma (caused by bacterial infection) and Eumycetoma (caused by fungal infection). Actinomycetoma can be treated with antibiotics, with more than 90% success rate. On the other hand, while azole anti-fungal drugs can be used to treat Eumycetoma, the effectiveness is limited often resulting in recurrence and surgery or amputation of limbs.
4. About Malaria
Malaria, one of the three major infectious diseases, is caused by malaria parasites that are transmitted to people through the bite of an infected mosquito. According to the WHO, about the half of the world’s population is exposed to the risk of malaria, and there were an estimated 247 million malaria cases in 85 countries in 2021, of which about 620,000 lost their life. In particular, infants, children under the age of five, and pregnant women are more likely to develop serious illness and are always at risk of life-threatening conditions.2
Recently, strains of malaria which are resistant to existing medicines have been reported, and the development of a new medicine with a novel mechanism of action is an urgent priority. The majority of available antimalarial medicines target the blood-stage, in which the parasites replicate within erythrocytes, but medicines for the liver and transmission stages are limited. In order to completely cure malaria, prevent relapse, and prevent malaria being spread via mosquitoes, it is necessary to develop a new antimalarial medicine which targets all stages of the parasite lifecycle.
1 WHO Mycetoma http://www.who.int/buruli/mycetoma/en/
2 WHO Malaria https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/malaria

by codm | May 24, 2023 | Newsletter
For Print (PDF)
Eisai Co., Ltd. (Headquarters: Tokyo, CEO: Haruo Naito, “Eisai”) announced today the presentation of research across various types of cancer from its oncology portfolio and pipeline during the 2023 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting (#ASCO23), which is taking place virtually and in-person in Chicago, Illinois from June 2 to 6.
Notable research includes an oral presentation of results from the final pre-specified overall survival analysis of the pivotal Phase 3 CLEAR (Study 307)/KEYNOTE-581 trial, which evaluated lenvatinib (LENVIMA®) plus pembrolizumab (KEYTRUDA®) versus sunitinib for the first-line treatment of patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (Abstract #4502). A post hoc analysis from the REFLECT trial evaluating lenvatinib monotherapy versus sorafenib in the first-line treatment of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) will also be shared in a poster presentation (Abstract #4078).
“The outlook for advanced renal cell carcinoma has evolved in recent years, and the final analysis from the pivotal CLEAR trial to be presented at ASCO represents another step forward for patients and an opportunity to provide their physicians with long-term data,” said Dr. Takashi Owa, Chief Scientific Officer, Senior Vice President, Eisai Co., Ltd. “New data for lenvatinib and from our oncology pipeline showcase Eisai’s continued commitment to driving innovation and exploring novel therapeutic modalities in our ambition to live out our human health care concept, our corporate mission to meet the needs of more people who face a cancer diagnosis.”
Additional data from Eisai’s pipeline include a poster presentation of findings from a phase 1b study of E7386, a CREB-binding protein (CBP) / β-catenin interaction inhibitor, in combination with lenvatinib in patients with advanced HCC (Abstract #4075), and the small cell lung cancer cohort of a phase 1b/2 trial evaluating E7389-LF, a new liposomal formulation of eribulin, in combination with nivolumab (Abstract #8593). Insights from preclinical testing of farletuzumab ecteribulin (FZEC), formerly known as MORAb-202, and MORAb-109, antibody drug conjugates (ADC), in rare gynecologic cancers will also be published online (Abstract # e17634).
Furthermore, Bliss Biopharmaceutical Co., Ltd. (BlissBio) will present a poster at the conference with results from the first-in-human study of BB-1701, a HER2-targeting ADC (Abstract #3029). Eisai entered into a joint development agreement with BlissBio for BB-1701 with option rights for a strategic collaboration in April 2023. A Phase 1/2 clinical study of BB-1701 in the U.S. and China for HER2-expressing solid tumors is currently underway.
This release discusses investigational compounds and investigational uses for FDA-approved products. It is not intended to convey conclusions about efficacy and safety. There is no guarantee that any investigational compounds or investigational uses of FDA-approved products will successfully complete clinical development or gain FDA approval.
The full list of presentations is included below. These abstracts will be made available on Thursday, May 25, 2023 at 4:00 PM Central Daylight Time (CDT).
| Cancer Type |
Study/Compound |
Abstract Title |
Abstract Type & Details |
| Lenvatinib Plus Pembrolizumab |
| Gynecologic Cancer |
CLEAR |
Final prespecified overall survival (OS) analysis of CLEAR: 4-year follow-up of lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab (L+P) vs sunitinib (S) in patients (pts) with advanced renal cell carcinoma (aRCC) |
Oral Abstract Session
Abstract #4502
June 5, 2023
11:54 AM CDT
|
|
Lenvatinib
|
| Gastrointestinal Cancer |
REFLECT |
Efficacy of lenvatinib (LEN) vs sorafenib (SOR) in the first-line (1L) treatment of patients (pts) with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (uHCC): A post hoc analysis of patients with nonviral etiology from REFLECT |
Poster Session
Abstract #4078
June 5, 2023
8:00 AM CDT
|
| Pipeline |
| Lung Cancer |
E7389-LF |
Phase 2 small cell lung cancer (SCLC) cohort of a phase 1b/2 trial of a liposomal formulation of eribulin in combination with nivolumab |
Poster Session
Abstract #8593
June 4, 2023
8:00 AM CDT
|
| Gastrointestinal Cancers |
E7386 (plus lenvatinib) |
A phase 1b study of E7386, a CREB-binding protein (CBP)/β-catenin interaction inhibitor, in combination with lenvatinib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma |
Poster Session
Abstract #4075
June 5, 2023
8:00 AM CDT
|
| Gynecologic Cancer |
Farletuzumab Ecteribulin
(FZEC) |
Preclinical testing of farletuzumab ecteribulin (FZEC [MORAb-202]) and MORAb-109, folate receptor α and mesothelin targeting antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), in rare gynecologic cancers |
Online Publication
Abstract #e17634
May 25, 2023
4:00 PM CDT
|
| Solid tumors |
BB-1701
(Presented by BlissBio) |
A first-in-human, open label, multiple dose, dose escalation, and cohort expansion phase 1 study to investigate the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics and antitumor activity of BB-1701 in patients with locally advanced/metastatic HER2-expressing solid tumors |
Poster Session
Abstract #3029
June 3, 2023
8:00 AM CDT
|
| Additional Research |
| Pan-tumor |
Systematic review |
Anti-drug antibodies related to CTLA-4, PD-1 or PD-L1 inhibitors across tumour types: A systematic review |
Online Publication
Abstract #e14600
May 25, 2023
4:00 PM CDT
|
In March 2018, Eisai and Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA (known as MSD outside the United States and Canada), through an affiliate, entered into a strategic collaboration for the worldwide co-development and co-commercialization of lenvatinib, both as monotherapy and in combination with Merck’s anti-PD-1 therapy pembrolizumab. Eisai and Merck are studying the LENVIMA plus KEYTRUDA combination through the LEAP (LEnvatinib And Pembrolizumab) clinical program in various tumor types across more than multiple clinical trials.
In June 2021, Eisai and Bristol Myers Squibb entered into an exclusive global strategic collaboration agreement for the co-development and co-commercialization of farletuzumab ecteribulin (FZEC, formerly known as MORAb-202), a folate receptor alpha (FRα)-targeting ADC. Eisai and Bristol Myers Squibb are currently investigating FZEC in multiple studies including: a Phase 1/2 clinical study in the United States and Europe for solid tumors including endometrial cancer, a Phase 2 clinical study in the United States and Europe for non-small cell lung cancer, and a Phase 2 clinical study in Japan, the United States and Europe for ovarian cancer, peritoneal cancer and fallopian tube cancer.
Media Inquiries:
Public Relations Department,
Eisai Co., Ltd.
+81-(0)3-3817-5120
[Notes to editors]
1. Eisai’s Focus on Cancer
Eisai acknowledges “Oncology” as one of its key strategic areas, and will continue to focus on the discovery and development of anti-cancer drugs within drug discovery domains including “tumor microenvironment”, “proteostasis disruption”, “cell linage and cell differentiation”, and “inflammation, hypoxia, oxidative stress and cell senescence” under the Deep Human Biology Learning (DHBL) drug discovery and development organization. Eisai aspires to discover innovative new drugs with new targets and mechanisms of action from these domains with the aim of contributing to the cure of cancers.
* KEYTRUDA® is a registered trademark of Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC., a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA.

by codm | May 22, 2023 | Newsletter
For Print (PDF)
INVESTOR, PHARMACEUTICAL AND TRADE MEDIA INFORMATION ONLY. THIS PRESS RELEASE IS NOT FOR A UK AUDIENCE.
TOKYO and CAMBRIDGE, Mass., May 22, 2023 – Eisai Co., Ltd. (Headquarters: Tokyo, CEO: Haruo Naito, “Eisai”) and Biogen Inc. (Nasdaq: BIIB, Corporate headquarters: Cambridge, Massachusetts, CEO: Christopher A. Viehbacher, “Biogen”) announced today that Eisai has submitted a Marketing Authorization Application (MAA) for lecanemab, an investigational anti-amyloid beta (Aβ) protofibril antibody, for the treatment of early Alzheimer’s disease (mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and mild AD dementia) with confirmed amyloid pathology in the brain, to the UK Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) in Great Britain. Lecanemab has been designated by the MHRA for the Innovative Licensing and Access Pathway (ILAP).
The MAA is based on the results of the confirmatory Phase III Clarity AD study and Phase IIb clinical study (Study 201), which demonstrated that lecanemab treatment showed a reduction of clinical decline in early AD, and is subject to a validation to determine whether it will be accepted by the MHRA. Lecanemab selectively binds and eliminates soluble, toxic Aβ aggregates (protofibrils) that are thought to contribute to the neurotoxicity in AD. As such, lecanemab may have the potential to have an effect on disease pathology and the progression of the disease. The Clarity AD study of lecanemab met its primary endpoint and all key secondary endpoints with highly statistically significant results.
Eisai serves as the lead of lecanemab development and regulatory submissions globally with both Eisai and Biogen co-commercializing and co-promoting the product and Eisai having final decision-making authority.
Contacts:
| Eisai |
Biogen Inc. |
MEDIA CONTACT:
Eisai Co., Ltd.
Public Relations Department
TEL: +81 (0)3-3817-5120
Eisai Inc. (U.S.)
Libby Holman
TEL: + 1-201-753-1945
Libby_Holman@eisai.com
Eisai Europe, Ltd.
(Europe, Australia, New Zealand and Russia)
EMEA Communications Department
TEL: +44-(0) 786 601 1272
EMEA-comms@eisai.net
INVESTOR CONTACT:
Eisai Co., Ltd.
Investor Relations Department
TEL: +81 (0) 3-3817-5122 |
MEDIA CONTACT:
Jack Cox
+ 1-210-544-7920
public.affairs@biogen.com
INVESTOR CONTACT:
Chuck Triano
+ 1-781-464-2442
IR@biogen.com |
[Notes to editors]
1. About the Innovative Licensing and Access Pathway (ILAP) in the UK
The ILAP is a program offered by the MHRA (UK) for development programs with the goal of reducing the time to market for innovative medicines that treat life-threatening or seriously debilitating conditions and/or conditions for which there is a significant unmet patient need. The ILAP aims to achieve this goal by enabling enhanced coordination between sponsors, the MHRA and reimbursement bodies such as National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE), leading up to Marketing Authorization Application (MAA) submissions to support accelerated access.
2. About Lecanemab
Lecanemab is the result of a strategic research alliance between Eisai and BioArctic. It is a humanized immunoglobulin gamma 1 (IgG1) monoclonal antibody directed against aggregated soluble (protofibril) and insoluble forms of amyloid-beta (Aβ).
In the U.S., lecanemab was granted accelerated approval for Alzheimer’s disease (AD) by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) on January 6, 2023. On the same day, Eisai submitted a supplemental Biologics License Application (sBLA) to the FDA for approval under the traditional pathway. This application was accepted, and has been granted Priority Review, with a Prescription Drug User Fee Act (PDUFA) action date of July 6, 2023. In Europe, Eisai submitted a MAA to the European Medicines Agency (EMA) on January 9, 2023, which was accepted on January 26, 2023. In Japan, Eisai submitted a Marketing Authorization Application to the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) on January 16, 2023, and Priority Review was designated by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW) on January 26, 2023. In China, Eisai initiated submission of data for a BLA to the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) of China in December 2022, which was designated for Priority Review on February 27, 2023. In Canada, Eisai submitted a New Drug Submission (NDS) to Health Canada on March 31, 2023, and was accepted on May 15 of the same year.
Lecanemab is indicated for the treatment of AD in the U.S. Treatment with lecanemab should be initiated in patients with mild cognitive impairment or mild dementia stage of disease, the population in which treatment was initiated in clinical trials. There are no safety or effectiveness data on initiating treatment at earlier or later stages of the disease than were studied. This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on reduction in Aβ plaques observed in patients treated with lecanemab. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification of clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial.
Eisai has completed a lecanemab subcutaneous bioavailability study, and subcutaneous dosing is currently being evaluated in the Clarity AD OLE.
Since July 2020 the Phase III clinical study (AHEAD 3-45) for individuals with preclinical AD, meaning they are clinically normal and have intermediate or elevated levels of amyloid in their brains, is ongoing. AHEAD 3-45 is conducted as a public-private partnership between the Alzheimer’s Clinical Trial Consortium that provides the infrastructure for academic clinical trials in AD and related dementias in the U.S, funded by the National Institute on Aging, part of the National Institutes of Health, Eisai and Biogen. The Tau NexGen clinical study for Dominantly Inherited AD (DIAD), that is conducted by Dominantly Inherited Alzheimer Network Trials Unit (DIAN-TU), led by Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, has been ongoing since January 2022.
3. About the Collaboration between Eisai and Biogen for AD
Eisai and Biogen have been collaborating on the joint development and commercialization of AD treatments since 2014. Eisai serves as the lead of lecanemab development and regulatory submissions globally with both companies co-commercializing and co-promoting the product and Eisai having final decision-making authority.
4. About the Collaboration between Eisai and BioArctic for AD
Since 2005, Eisai and BioArctic have had a long-term collaboration regarding the development and commercialization of AD treatments. Eisai obtained the global rights to study, develop, manufacture and market lecanemab for the treatment of AD pursuant to an agreement with BioArctic in December 2007. The development and commercialization agreement on the antibody lecanemab back-up was signed in May 2015.
5. About Eisai Co., Ltd.
Eisai’s Corporate Concept is “to give first thought to patients and people in the daily living domain, and to increase the benefits that health care provides.” Under this Concept (also known as human health care (hhc) Concept), we aim to effectively achieve social good in the form of relieving anxiety over health and reducing health disparities. With a global network of R&D facilities, manufacturing sites and marketing subsidiaries, we strive to create and deliver innovative products to target diseases with high unmet medical needs, with a particular focus in our strategic areas of Neurology and Oncology.
In addition, we demonstrate our commitment to the elimination of neglected tropical diseases (NTDs), which is a target (3.3) of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), with working on various activities together with global partners.
For more information about Eisai, please visit www.eisai.com (for global headquarters: Eisai Co., Ltd.), and connect with us on Twitter, LinkedIn and Facebook. For more information about Eisai in the EMEA region please visit www.eisai.eu.
6. About Biogen
Founded in 1978, Biogen is a leading global biotechnology company that has pioneered multiple breakthrough innovations including a broad portfolio of medicines to treat multiple sclerosis, the first approved treatment for spinal muscular atrophy, and two co-developed treatments to address a defining pathology of Alzheimer’s disease. Biogen is advancing a pipeline of potential novel therapies across neurology, neuropsychiatry, specialized immunology and rare diseases and remains acutely focused on its purpose of serving humanity through science while advancing a healthier, more sustainable and equitable world.
The company routinely posts information that may be important to investors on its website. Follow Biogen on social media – Twitter, LinkedIn, Facebook, YouTube.
Biogen Safe Harbor
This news release contains forward-looking statements, including statements made pursuant to the safe harbor provisions of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995, about the potential clinical effects of lecanemab; the potential benefits, safety and efficacy of lecanemab; potential regulatory discussions, submissions and approvals and the timing thereof; the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease; the anticipated benefits and potential of Biogen’s collaboration arrangements with Eisai; the potential of Biogen’s commercial business and pipeline programs, including lecanemab; and risks and uncertainties associated with drug development and commercialization. These statements may be identified by words such as “aim,” “anticipate,” “believe,” “could,” “estimate,” “expect,” “forecast,” “intend,” “may,” “plan,” “possible,” “potential,” “will,” “would” and other words and terms of similar meaning. Drug development and commercialization involve a high degree of risk, and only a small number of research and development programs result in commercialization of a product. Results in early-stage clinical studies may not be indicative of full results or results from later stage or larger scale clinical studies and do not ensure regulatory approval. You should not place undue reliance on these statements or the scientific data presented.
These statements involve risks and uncertainties that could cause actual results to differ materially from those reflected in such statements, including without limitation unexpected concerns that may arise from additional data, analysis or results obtained during clinical studies, including the Clarity AD clinical trial and AHEAD 3-45 study; the occurrence of adverse safety events; risks of unexpected costs or delays; the risk of other unexpected hurdles; regulatory submissions may take longer or be more difficult to complete than expected; regulatory authorities may require additional information or further studies, or may fail or refuse to approve or may delay approval of Biogen’s drug candidates, including lecanemab; actual timing and content of submissions to and decisions made by the regulatory authorities regarding lecanemab; uncertainty of success in the development and potential commercialization of lecanemab; failure to protect and enforce Biogen’s data, intellectual property and other proprietary rights and uncertainties relating to intellectual property claims and challenges; product liability claims; third party collaboration risks; and the direct and indirect impacts of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic on Biogen’s business, results of operations and financial condition. The foregoing sets forth many, but not all, of the factors that could cause actual results to differ from Biogen’s expectations in any forward-looking statement. Investors should consider this cautionary statement as well as the risk factors identified in Biogen’s most recent annual or quarterly report and in other reports Biogen has filed with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. These statements speak only as of the date of this press release. We do not undertake any obligation to publicly update any forward-looking statements.

by codm | May 17, 2023 | Newsletter
For Print (PDF)
Eisai Co., Ltd. (Headquarters: Tokyo, CEO: Haruo Naito, “Eisai”) today announced the publication of results from a simulation study evaluating the societal value of anti-amyloid-beta (Aβ) protofibril* antibody lecanemab (generic name, U.S. brand name: LEQEMBI™) in individuals living with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) due to Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and mild AD dementia (collectively known as early AD) in the context of the Japanese health care system in the peer-reviewed journal Neurology and Therapy. The paper concluded that lecanemab treatment would improve health and humanistic (quality of life) outcomes and reduce economic burden for individuals with early AD and their caregivers in Japan.
This model-based simulation was conducted using data from the Phase 3 Clarity AD study evaluating the efficacy and safety of lecanemab for early AD with confirmed amyloid pathology by applying an academically validated disease simulation model (AD Archimedes Condition Event simulation: AD ACE model1,2) as well as government statistics, including Japanese epidemiological data and fact-finding surveys on long-term care, and other past research articles to take into account the environment under the Japanese healthcare system from the healthcare payer’s perspective, focusing on direct care costs (including out- and in-patient services, nursing- and home-health- care services, cost of medications, and other intervention costs) and the societal perspective (social costs including informal care costs such as family nursing care in addition to direct care costs). In this paper, the cost reduction effect of lecanemab and the improvement in health outcomes were integrated, incorporating the former cost reduction effect as is, while the latter outcome improvement effect was estimated based on previous studies in the U.S. and the benchmark price estimation process of the U.S. Institute for Clinical and Economic Review (ICER).
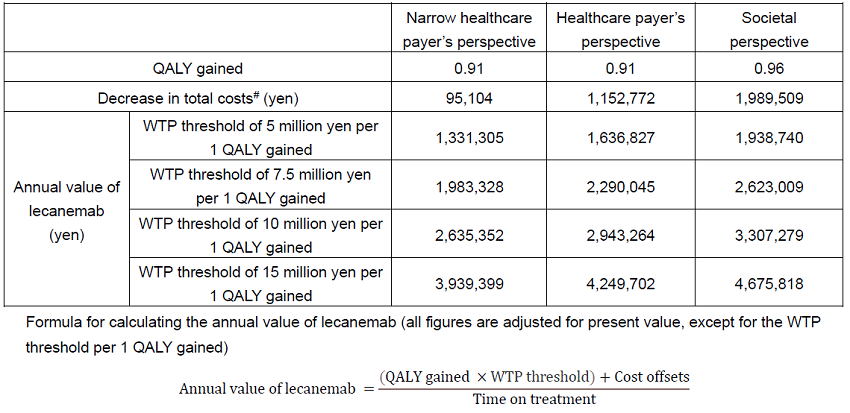
The analysis predicted an increase in Quality-Adjusted Life-Years** (QALYs) by 0.91 from both the narrow healthcare payer’s perspective (considering only medical treatment costs) and the healthcare payer’s perspective (medical treatment and public care costs) (SoC (standard of care***): 6.12, lecanemab+SoC (lecanemab treatment with SoC): 7.03). From the societal perspective, the increase in QALYs was estimated to be 0.96 (SoC: 5.78, lecanemab+SoC: 6.74) compared to SoC. In addition, compared to SoC alone, lecanemab+SoC was predicted to result in a decrease in total costs of 95,104 yen from the narrow healthcare payer’s perspective (SoC: 2,793,491 yen, lecanemab+SoC: 2,698,387: yen), 1,152,772 yen from the healthcare payer’s perspective (SoC: 11,381,044 yen, lecanemab+SoC: 10,228,272 yen), and 1,989,509 yen from the societal perspective (SoC: 24,482,321 yen, lecanemab+SoC 22,492,811 yen). The estimated mean duration of lecanemab treatment was 3.68 years in this simulation.
While taking into account the above factors, the model estimated that the annual value of lecanemab was 1,331,305 yen to 3,939,399 yen from the narrow healthcare payer’s perspective, 1,636,827 yen to 4,249,702 yen from the healthcare payer’s perspective, and 1,938,740 yen to 4,675,818 yen from the societal perspective at the willingness-to-pay (WTP) threshold of 5 million yen to 15 million yen, per 1 QALY gained under the Japanese healthcare system. Regarding the WTP threshold to be paid per 1 QALY gained, an academic article has proposed that 5 times per capita gross domestic product (GDP) is appropriate for severe AD,3 and from an international perspective, it is thought that for common diseases other than AD, the WTP threshold per 1 QALY gained is equivalent to 1-3 times per capita GDP. Considering the above, this paper evaluated that 15 million yen per 1 QALY is appropriate as the WTP threshold for assessing the societal value of lecanemab.
Since AD has a huge impact not only on medical costs but also public care costs as well as the invisible burden including family care, it is important to recognize the societal value, and this paper showed that annual value of lecanemab from the societal perspective can be up to 4,675,818 yen.
Health outcomes (QALYs) and decrease in total costs from lecanemab treatment, and annual value of lecanemab
“Approximately 50% of public long-term care insurance finances in Japan are spent on care costs due to AD (public long-term care insurance finances: 9,626.6 billion yen; public long-term care costs due to AD: 4,783.2 billion yen in 2018). It is understood that AD has a significant impact on not only medical costs but also long-term care insurance finance and the costs due to AD increases significantly with the progression of the pathological stage, and when comparing MCI and severe dementia, medical costs and long-term care costs increase significantly by about 2 times and 10 times, respectively.4 The simulation results show that, in Japan, treatment with lecanemab can have a significant impact on caregivers and society as a whole by improving delaying disease progression”, said Masatomi Akana, Senior Vice President, Chief Government Relations Officer, and Global Value & Access Eisai Co., Ltd., “We believe that this paper will be important information for stakeholders to better understand the potential clinical and socio-economic value of lecanemab in Japan, as well as for discussions on the evaluation of innovation by pharmaceutical companies. We will continue to release data and information transparently and promptly in order to deliver lecanemab to eligible early AD patients.”
“This paper followed the U.S. methodology, and added country-specific conditions to estimate the societal value of the medicine in Japan” said the first author of this paper, Dr. Ataru Igarashi, Associate Professor of Medicine at Yokohama City University and Visiting Associate Professor of Pharmaceutical Policy at the University of Tokyo Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences. “When assessing the value of medicines, not only for dementia but for all diseases, I believe that in addition to efficacy, safety and treatment cost, various other aspects should be taken into account, such as the impact on work and the degree of burden reduction for family members and medical personnel.”
Eisai serves as the lead of lecanemab development and regulatory submissions globally with both companies co-commercializing and co-promoting the product and Eisai having final decision-making authority.
* Protofibrils are large Aβ aggregated soluble species of 75-5000 Kd.5
** The quality-adjusted life year (QALY) is a measure of the value of health outcomes. Since health is a function of length of life (i.e., quantity) and quality of life (QOL), the QALY was developed as an attempt to combine the value of these attributes into a single index number. One QALY equates to one year in perfect health. QOL scores range from 1 (full health) to 0 (dead). For example, if a new treatment and an existing treatment both increase survival years by 3 years, but the new treatment maintains a QOL of 0.7 (QALY=2.1), while the existing treatment has a lower QOL of 0.5 (QALY=1.5), the incremental QALY for the new treatment would be 0.6 (QALY = QOL score x survival years).
*** Standard of Care (SoC) for AD currently consists of lifestyle modifications and pharmacologic treatment of symptoms.
1 Tahami Monfared AA, Tafazzoli A, Ye W, Chavan A, Zhang Q. Long-Term Health Outcomes of Lecanemab in Patients with Early Alzheimer’s Disease Using Simulation Modeling. Neurology and therapy. 2022;11(2):863-80.
2 Tahami Monfared AA, Tafazzoli A, Chavan A, Ye W, Zhang Q. The Potential Economic Value of Lecanemab in Patients with Early Alzheimer’s Disease Using Simulation Modeling. Neurology and Therapy. 2022;11(3):1285-307.
3 Lakdawalla DN, Phelps CE. Health technology assessment with risk aversion in health. J Health Econ. 2020;72:102346. doi: 10.1016/j.jhealeco.2020.102346
4 S. Ikeda, M. Mimura, M. Ikeda, K .Wada-Isoe, M. Azuma, S. Inoue, K. Tomita. Economic Burden of Alzheimer’s Disease Dementia in Japan. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease 81(2021)309-319
5 Söderberg, L., Johannesson, M., Nygren, P. et al. Lecanemab, Aducanumab, and Gantenerumab — Binding Profiles to Different Forms of Amyloid-Beta Might Explain Efficacy and Side Effects in Clinical Trials for Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurotherapeutics (2022).
Media Inquiries:
Public Relations Department,
Eisai Co., Ltd.
+81-(0)3-3817-5120
Eisai Inc (U.S.)
Libby Holman
201-753-1945
Libby_Holman@eisai.com
[Notes to editors]
1. About Lecanemab
Lecanemab (brand name in the U.S.: LEQEMBI™) is the result of a strategic research alliance between Eisai and BioArctic. Lecanemab is a humanized immunoglobulin gamma 1 (IgG1) monoclonal antibody directed against aggregated soluble (protofibril) and insoluble forms of amyloid-beta (Aβ). In the U.S., LEQEMBI was granted accelerated approval by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) on January 6, 2023. LEQEMBI is indicated for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) in the U.S. Treatment with LEQEMBI should be initiated in patients with mild cognitive impairment or mild dementia stage of disease, the population in which treatment was initiated in clinical trials. There are no safety or effectiveness data on initiating treatment at earlier or later stages of the disease than were studied. This indication is approved in the U.S. under Accelerated Approval based on reduction in Aβ plaques observed in patients treated with LEQEMBI. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification of clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial.
Please see full Prescribing Information in the United States.
In the U.S., Eisai submitted a supplemental Biologics License Application (sBLA) to the FDA for approval under the traditional pathway on January 6, 2023. On March 3, 2023, the FDA accepted Eisai’s sBLA based on the Clarity AD clinical data, and the LEQEMBI application has been granted Priority Review, with a Prescription Drug User Fee Act (PDUFA) action date of July 6, 2023. The FDA is planning to hold an Advisory Committee to discuss this application on June 9, 2023. Eisai submitted an application for manufacturing and marketing approval to the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) on January 16, 2023, in Japan. The Priority Review was granted by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW) on January 26, 2023. Eisai utilized the prior assessment consultation system of PMDA, with the aim of shortening the review period for lecanemab. In Europe, Eisai submitted a marketing authorization application (MAA) to the European Medicines Agency (EMA) on January 9, 2023, and accepted on January 26, 2023. In China, Eisai initiated submission of data for a BLA to the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) of China in December 2022, and the Priority Review was granted on February 27, 2023. In Canada, Eisai submitted a New Drug Submission (NDS) to Health Canada on March 31, 2023, and was accepted on May 15 of the same year.
Eisai has completed lecanemab subcutaneous bioavailability study, and subcutaneous dosing is currently being evaluated in the Clarity AD (Study 301) OLE.
Since July 2020 the Phase 3 clinical study (AHEAD 3-45) for individuals with preclinical AD, meaning they are clinically normal and have intermediate or elevated levels of amyloid in their brains, is ongoing. AHEAD 3-45 is conducted as a public-private partnership between the Alzheimer’s Clinical Trial Consortium that provides the infrastructure for academic clinical trials in AD and related dementias in the U.S, funded by the National Institute on Aging, part of the National Institutes of Health, Eisai and Biogen.
Since January 2022, the Tau NexGen clinical study for Dominantly Inherited AD (DIAD), that is conducted by Dominantly Inherited Alzheimer Network Trials Unit (DIAN-TU), led by Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, is ongoing.
2. About the Collaboration between Eisai and Biogen for AD
Eisai and Biogen have been collaborating on the joint development and commercialization of AD treatments since 2014. Eisai serves as the lead of lecanemab development and regulatory submissions globally with both companies co-commercializing and co-promoting the product and Eisai having final decision-making authority.
3. About the Collaboration between Eisai and BioArctic for AD
Since 2005, Eisai and BioArctic have had a long-term collaboration regarding the development and commercialization of AD treatments. Eisai obtained the global rights to study, develop, manufacture and market lecanemab for the treatment of AD pursuant to an agreement with BioArctic in December 2007. The development and commercialization agreement on the antibody lecanemab back-up was signed in May 2015.







